Electroneurogram (ENG)
Αρχική / Neurophysiological Laboratory / Electroneurogram
Information
for the examination
Basic elements:
- The Electroneurogram examines the functional state of peripheral nerves .
- It is a outpatient examination, which the Neurologist is trained to use as an extension of the patient’s clinical examination, when required .
- It is very important for the study and diagnosis mainly of various diseases of the peripheral nervous system , such as polyneuropathy or mononeuritis (damage to only one nerve). Also when the nerve roots are injured during, or after their exit from the spine (such as in disc diseases).
What are the symptoms?
With the ENG they can to investigate symptoms such as:
- Acute the chronic pain (eg waist, neck, shoulder, torso)
- Blood clots, heartburn (on hands, feet or face).
- Gait instability
- Clumsy movement of hands and feet
- Weaknesses, paralysis (hand, foot, face and elsewhere)
- Muscle atrophies
When does one need to seek the help of a specialist?
The neurologist depending on the clinical condition of the patient, will recommend the performance of the specific outpatient examination.
The Electroneurogram in combination most often with the electromyogram carried out in the following cases :
- when the cause of the paralysis is sought in a muscle or group of muscles
- when δι numbness is investigated on the hands or feet
- when we clinically suspect pressure on a nerve
- when there is pressure on the spinal cord (eg in cervical myelopathy)
- in neural network diseases
- in muscle diseases (eg myopathy, myasthenia)
Examination
What is the patient's preparation before the examination?
No special preparation is required for the examination . But it can to follow some general rules before the examination .
- Make sure you wear comfortable clothes before leaving the house
- Do not apply cream, lotion or other oils on the skin on the day of the examination
The patient informs the doctor if:
- It has a pacemaker
- He suffers from a condition that affects blood clotting,
- He has had Botox injections
- Takes antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs
- Takes drugs that affect mobility (eg muscle relaxants)
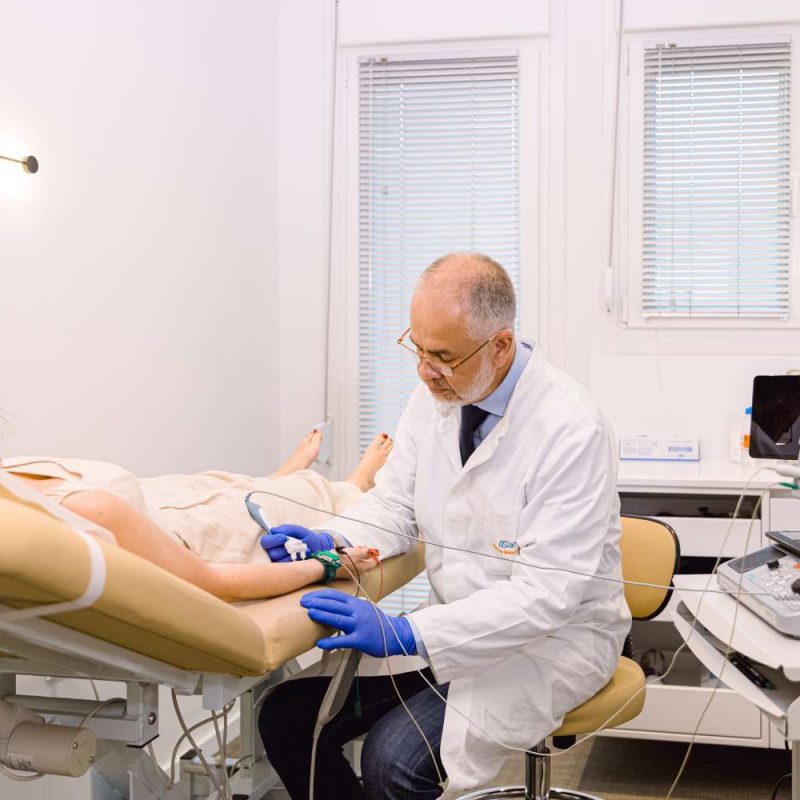
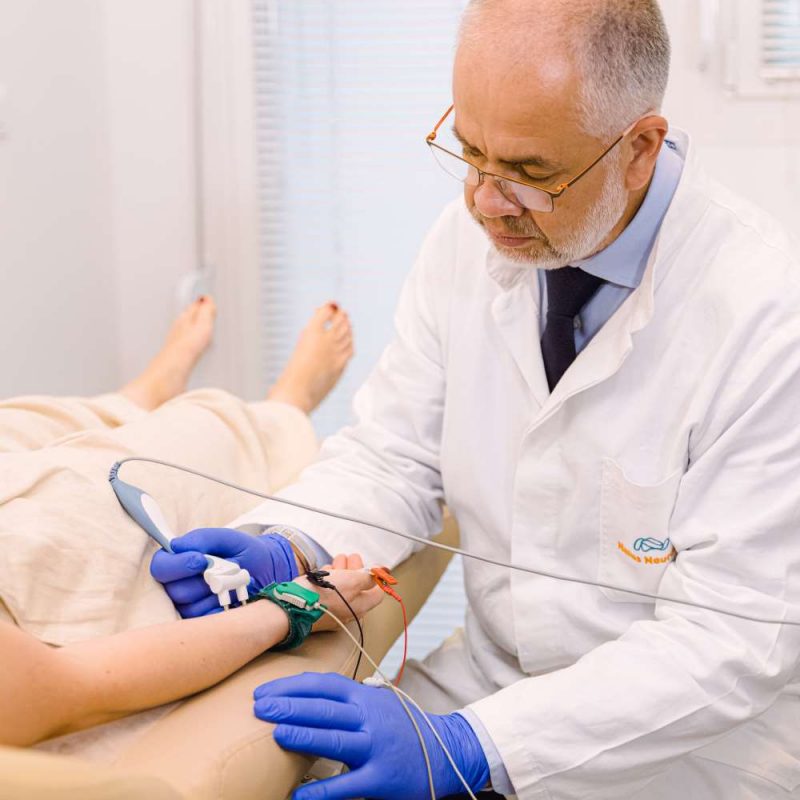
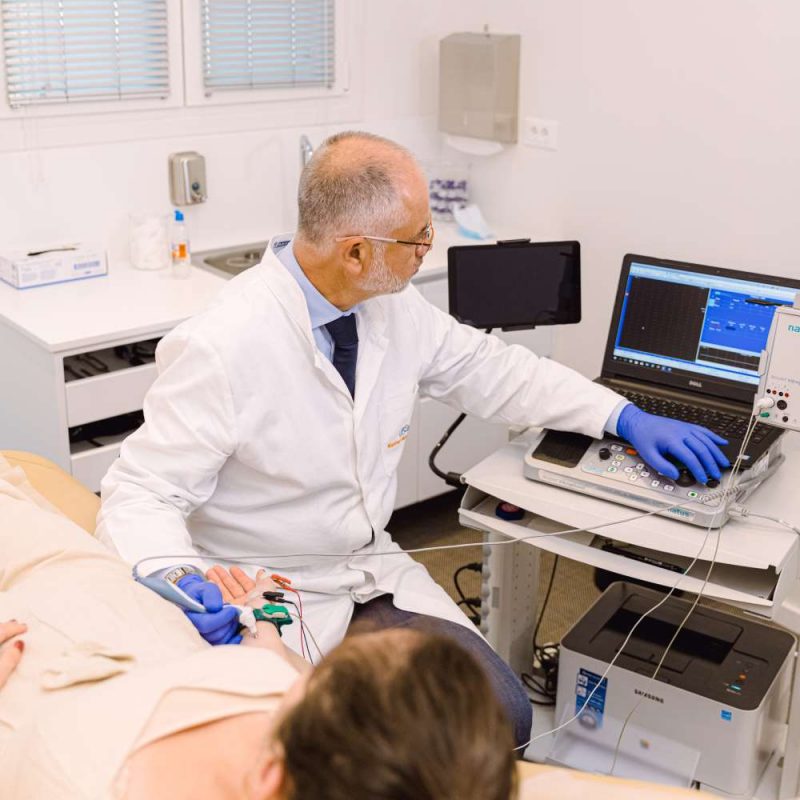
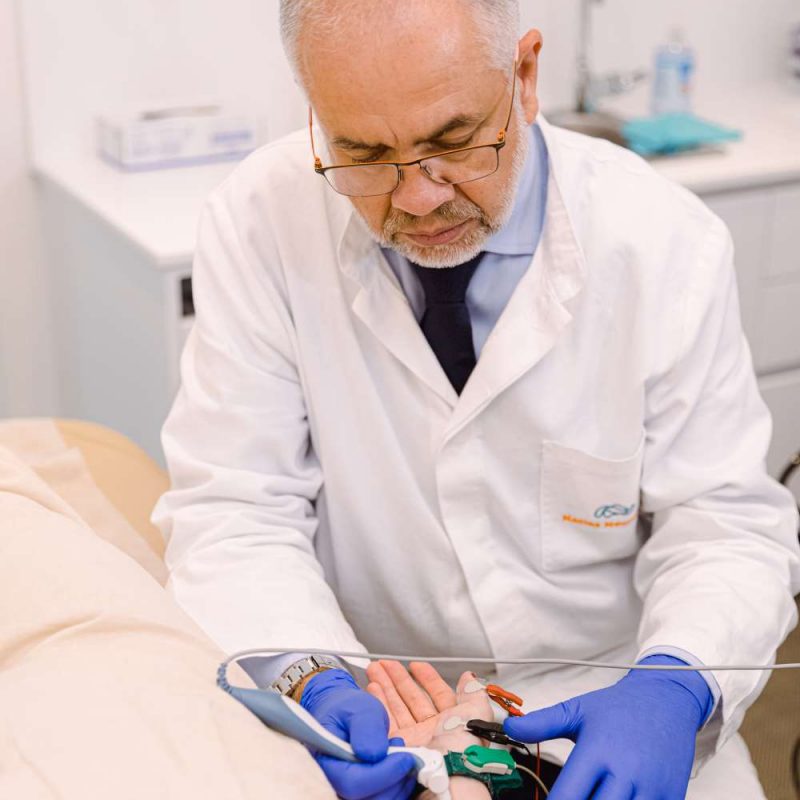
How is the test performed?
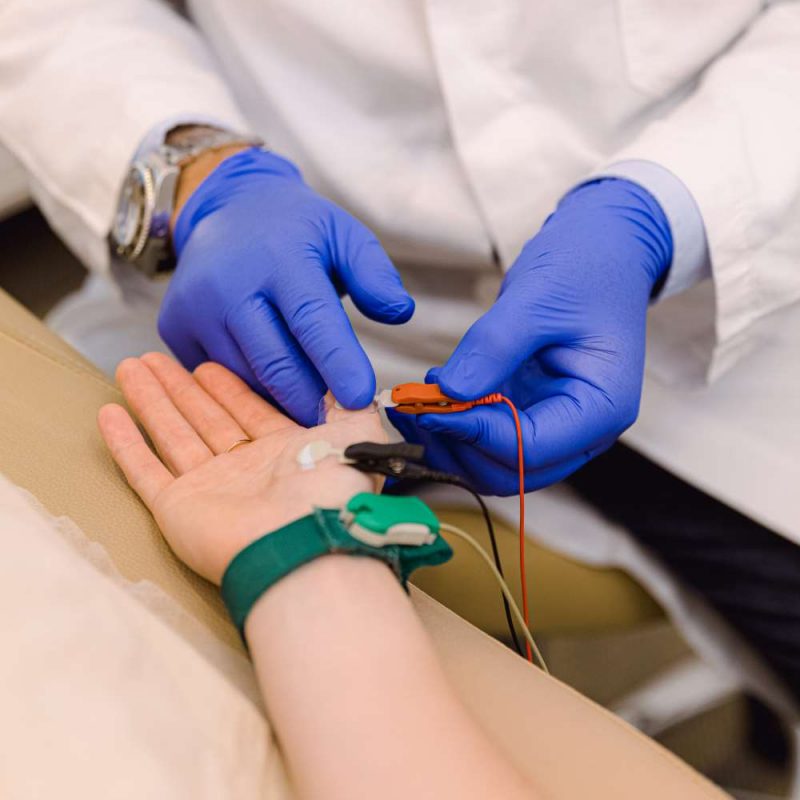
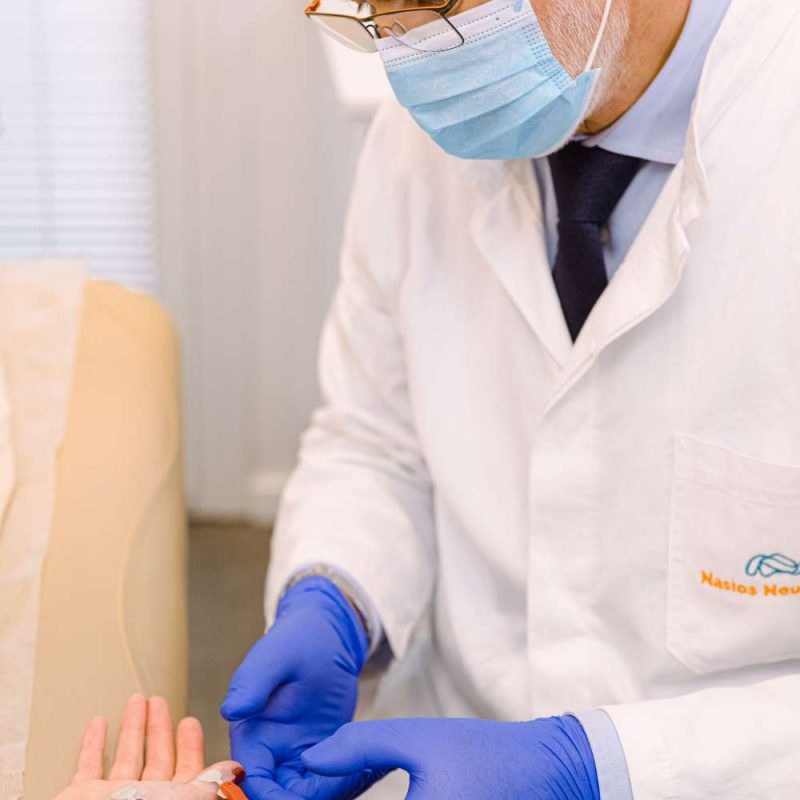
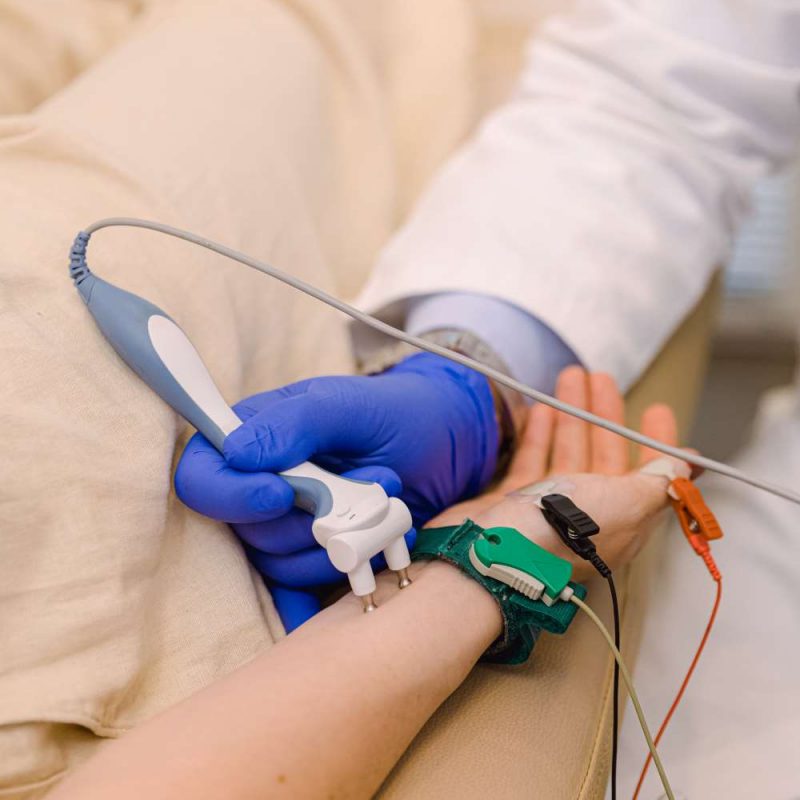
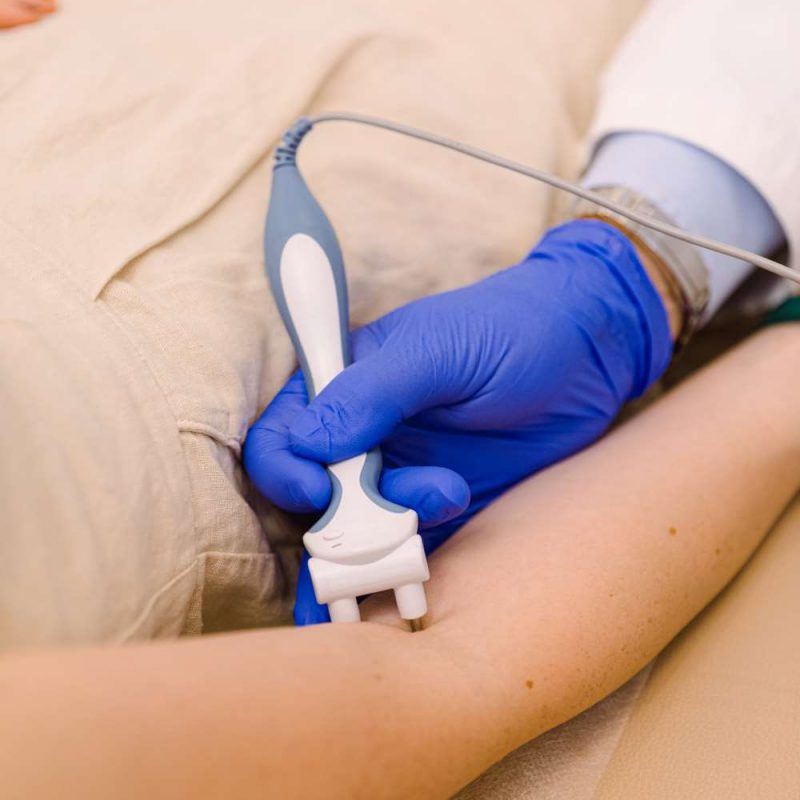
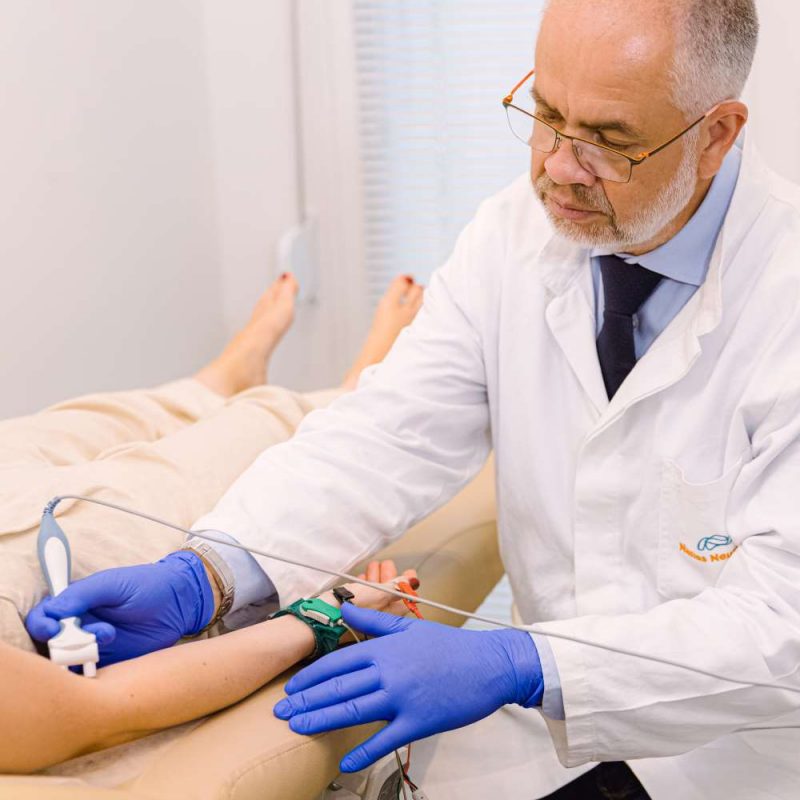
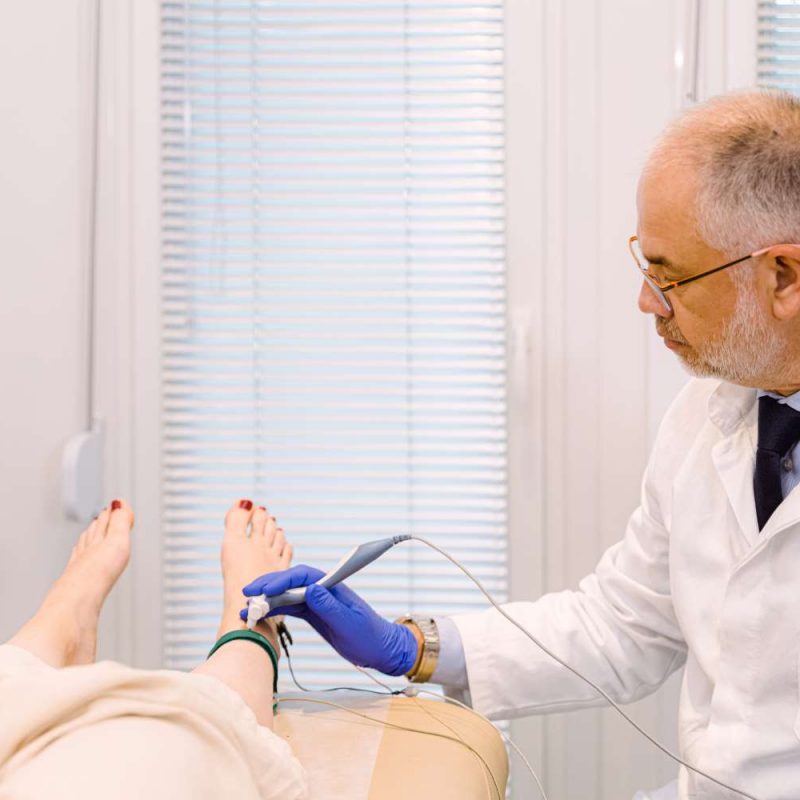
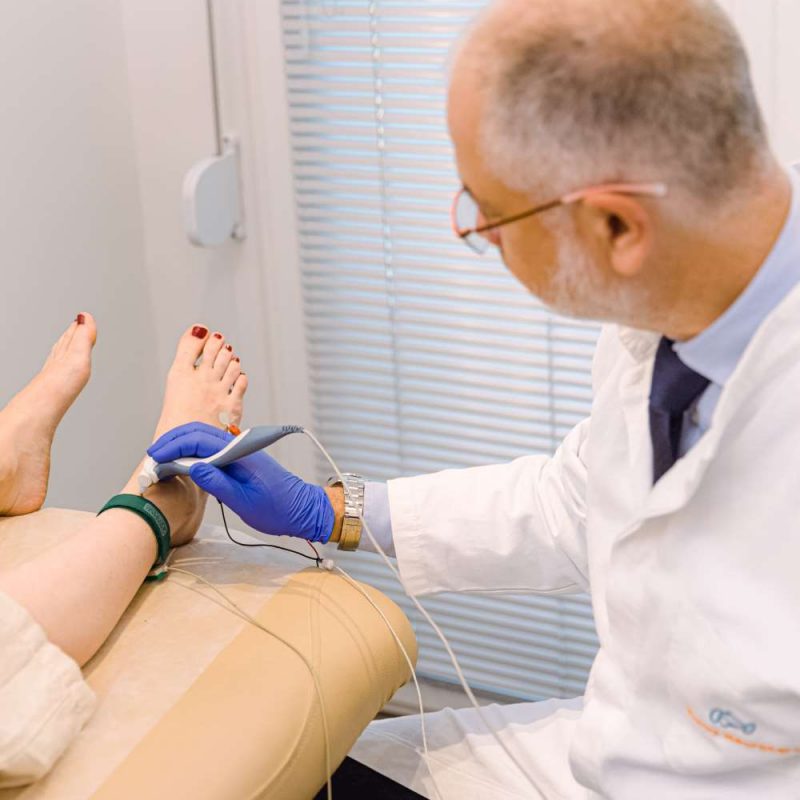
During the examination:
- are placed surface electrodes at specific points of the body
- if the temperature of its edges is low then heated first
- follows mild electrical irritation of the nerves (which are like the “cables” of our body)
- the choice of points depends from which nerve the patient’s symptoms need to be controlled. Simultaneously with the help of other electrodes the potentials created by muscle contraction are recorded which are innervated by the corresponding nerves
Can there be complications from the test?
- The electroneurogram is generally a safe and uncomplicated test .
- In a minority of patients There is a sensitivity to electrical stimulation or to the insertion of a needle into a muscle